From Delays to Delivery: Kanban Optimizes Inventory & Boosts Profits for Machine Manufacturing
Introduction:
Kanban Transforms Machine Manufacturing: From Chaos to Cost Savings. Our client Machine Manufacturing is a medium-sized company specializing in the production of industrial machinery for plastic processing. They have a diverse product line ranging from Extruder machines to automatic machines used in various plastic industries such as beverages, chemicals etc.
Challenges:
- Inventory Management: The company faces challenges in managing inventory levels of components and parts used in machine manufacturing.
- Production Delays: There are frequent delays in production due to a lack of visibility into the status of work orders and bottlenecks in the manufacturing process.
- Overproduction: Occasional overproduction of certain components leading to increased inventory costs and waste and space occupation.
So, we took the project of kanban to manage inventory.
Implementation of Kanban:
Phase 1 : Planning and Preparation
- Stakeholder Alignment: The management team and production staff are briefed about the concept and benefits of Kanban.
- A Class items list: A cross-functional team lists out the items that are critical to production.
- Defining Workflows: Workflows are defined for each stage of production, from raw material procurement to finished product assembly.
Phase 2 : Implementation
- Visualizing Workflows: Kanban boards are set up in key production areas to visually represent the workflow stages. Each stage is represented by columns such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.”
- Limiting Work in Progress (WIP): WIP limits are established by us for each stage to prevent overloading and to maintain a smooth flow of work.
- Inventory Management: Kanban cards are used to track inventory levels of components. When inventory reaches a predefined minimum threshold, a signal is sent to replenish stock.
Phase 3 : Monitoring & Improvement
- Daily Stand-up Meetings: We prepared a daily meeting schedule so Daily meetings are held where teams review progress, identify bottlenecks, and adjust the Kanban board as needed.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular retrospectives are conducted to gather feedback from teams and implement process improvements.
- Integration with Suppliers: Kanban is extended to suppliers, allowing for a pull-based system where suppliers replenish inventory based on actual demand.
Results Achieved :
- Improved Visibility: Kanban provides real-time visibility into the status of work orders and inventory levels, enabling better decision-making and reducing production delays.
- Reduced Lead Times: By limiting WIP and streamlining workflows, lead times are significantly reduced, allowing the company to respond more quickly to customer demands.
- Cost Savings: Reduced inventory holding costs due to optimized inventory levels and minimized overproduction.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Kanban fosters better collaboration and communication between different departments, leading to smoother production processes.
- Increased Efficiency: Overall, the implementation of Kanban has led to increased efficiency and productivity in machine manufacturing operations.
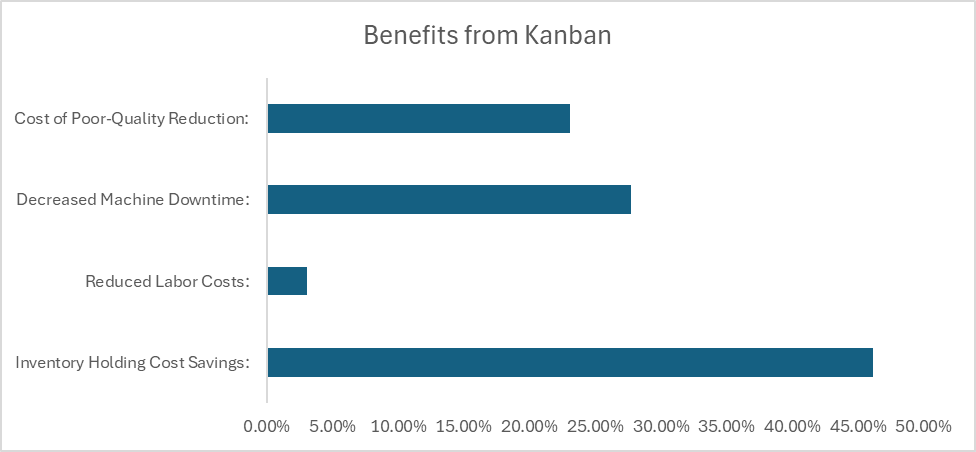
Monetary Benefits :
- Inventory Holding Cost Savings: $30000 per year.
- Reduced Labor Costs: $2,000 per year
- Decreased Machine Downtime: $18000 per year.
- Cost of Poor-Quality Reduction: $15000 per year
- Overall Cost Savings: $2000 + $30000 + $18000+ $15000 =$65000 Total Annual Savings
By quantifying these monetary benefits, Machine manufacturers can assess the return on investment (ROI) of implementing Kanban and justify the expenditure on process improvement initiatives.